GEO vs SEO - What Beginners Must know to Rank in AI Search
TL;DR
This article explains the key differences between SEO (optimizing for search engines through keywords, links, and ranking factors) and GEO (optimizing for AI tools like ChatGPT and Google’s SGE to deliver direct, conversational answers). While SEO drives clicks, GEO ensures citations in AI results. Adopting a hybrid approach helps content creators stay visible and competitive in the evolving digital landscape.
In the fast-paced digital world, it is now necessary to have an understanding of both SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and GEO (Generative Engine Optimization). SEO emphasizes visibility in more traditional search engines such as Google through the use of keyword optimization, backlinks, and technical optimization. Whereas GEO is the new form of tailoring content to AI-driven generative engines, such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other tools that answer queries directly rather than deliver lists of websites.
SEO optimizes the search algorithms, which rely heavily on web page indexing, while GEO optimizes conversational AI models, which place more emphasis on context, intent, and quality of the language. It is important to learn this difference since being ranked on Google does not necessarily lead to being chosen on generative AI platforms and vice versa. As a beginner, I suggest having the right way to produce the content that can be suitable to both, structured and search engine-friendly, but less formal and more informative to AI models. This article will cover key differences, practical methods, and best practices to enable you to become the best, and stay ahead in the new reality of multidimensional competition
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization, commonly known as SEO, is the process of improving a website or content that ranks higher on search engines like Google. When someone searches for information online, SEO helps your website to appear in the top search results, and makes it simple for people to find you. In simple terms, SEO involves optimizing your website’s content and technical aspects so that search engines can better understand and recommend it to users.
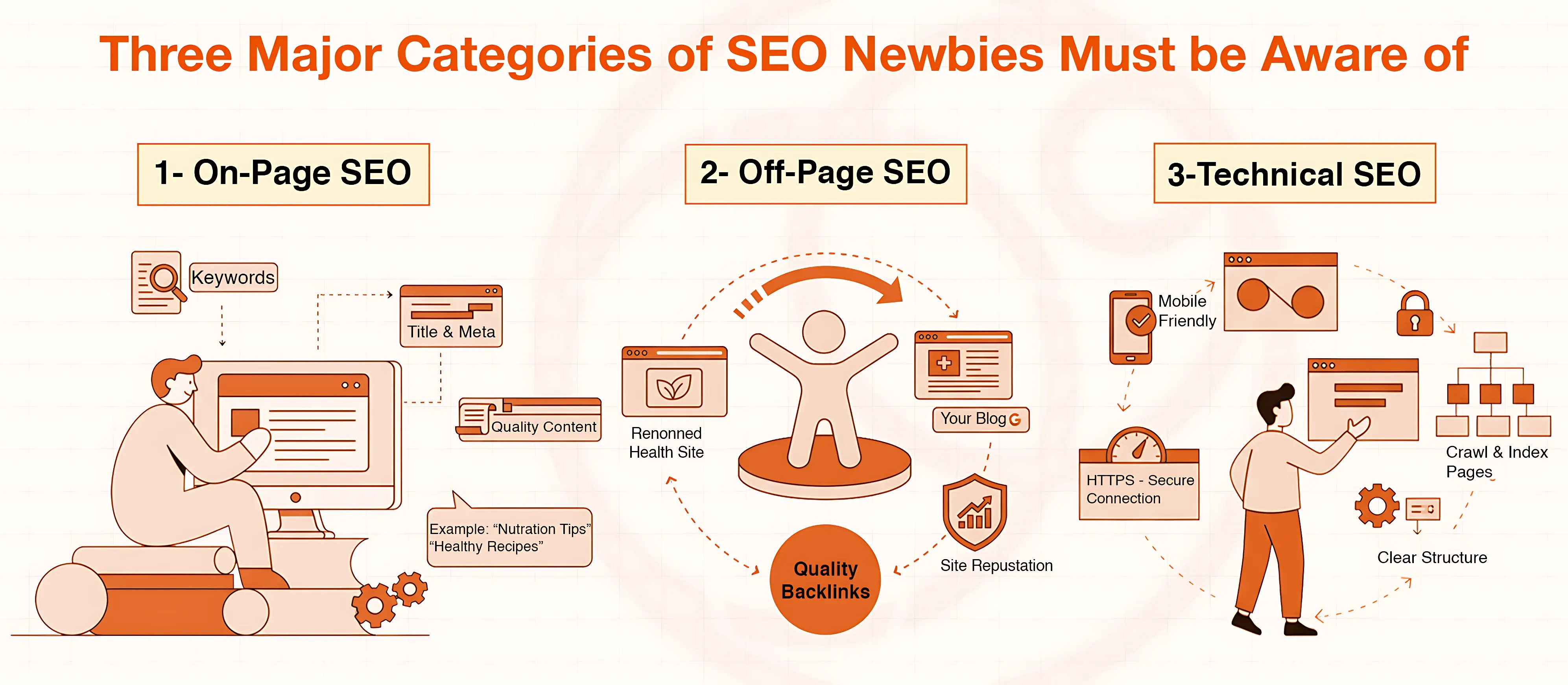
Three Major Categories of SEO Newbies Must be Aware of
1. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is about the content on your website. This involves proper keywords, quality articles, optimization of titles, meta descriptions, and content that should correspond to what people search. Example: In case you are writing about healthy eating, you need to use the terms in your content, like so-called nutrition tips or healthy recipes, as naturally as possible so that Google can understand what your page is all about.
2. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO deals with the trust level and popularity of your site to engines. The single biggest thing in this concern is the backlinks; links on other trusted sites that are directed to your site. The higher the number of quality backlinks that you possess, the better the reputation of the site is elevated. In an example, when a renowned health website links to your blog, Google receives the message that your content must be useful.
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO addresses the behind-the-scenes aspect of your site. This means site speed, mobile-friendliness, secure connection (HTTPS), and a clear structure that prioritizes ease of crawling and indexing of your pages by search engines. Even though you have good content, slow loading or a lack of compatibility with mobile devices can drag your rankings.
Beginners Example
- Consider you have a blog on healthy eating. To make it SEO friendly, you would:
- Optimise the use of on-page SEO by inserting keywords such as balanced diet and nutrition tips in your post.
- Use off-page SEO means getting backlinks to well-known health websites.
- Technical SEO will be strengthened by ensuring that your blog is fast and mobile-friendly.
With all three points, your blog stands a better opportunity of ranking high up Google search and attracting more readers.
What is GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
Generative Engine Optimization, or GEO, is a current digital marketing trend that involves optimizing content according to AI-based generative search engines. Unlike the older-style search engines, which would show a list of web pages, generative engines such as ChatGPT, Google Search Generative Experience (SGE), Gemini, Claude, and Perplexity instead present users with simplified answers in a conversational format that they have generated based on multiple sources. GEO works to help ensure that your content has a higher chance of being employed by these AI systems in their responses
Large language models (LLMs) that drive these AI tools are the principal targets of GEO. Such models process vast quantities of data and produce text answers that sound like humans. GEO is the process of tweaking your text to make it explicit, short, knowledgeable, and structured in a manner that AI engines can easily process and reference. This involves formatting material into short answer-ready paragraphs, simple language, and including quality references.
As an example, when a user prompts ChatGPT on the question concerning “generative AI in the context of SEO,” instead of providing links to websites, the AI may compile an answer that summarizes a collection of information referencing trusted sources. When your content is GEO-optimized, it is much more likely to render in that AI-generated answer, potentially raising your visibility, as well as increasing your authority.
GEO is gaining significance as AI search expands since it is altering the research profile of users. Where SEO emphasizes on ranking webpages on the search results, GEO here will specifically make sure that the AI can give accurate, helpful answers to the users. Content creators should think beyond keywords and traditional ranking signals to succeed. They should prioritize clarity and user intent aligned with how generative AI operates.
In brief, GEO integrates with SEO, making your content ready to go for the future of search.
Difference between GEO vs SEO — Quick Comparison
- Focus Area: SEO (Search Engine Optimization) focuses on the more conventional search engines, such as Google and Bing, and makes websites rank on the first pages of search results. GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) targets generative engines (such as ChatGPT and Search Generative Experience) that use AI to generate an answer, and optimize content to be included in the answer generated by the AI.
- Content Format: SEO depends on organized webpages that include keywords, backlinks, and metadata. GEO focuses on short, clear, and authoritative material, which is easy to process and can be referenced by AI.
- User Interaction: SEO caters to users who click on search results to explore webpages. GEO serves users by providing direct, conversational answers within AI interfaces without requiring clicks.
- Optimization Techniques: SEO uses keyword research, link-building, and technical SEO tactics. GEO involves creating concise paragraphs, adding citations, and structuring content for AI comprehension.
- Ranking Signals: SEO depends on backlinks, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and keyword relevance. GEO depends on content clarity, accuracy, and how well AI models understand and trust your content.
| Aspects | SEO | GEO |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Traditional search engines | AI powered generated engines |
| Content type | Webpages with keywords and links | Short, answer -ready paragraphs |
| User Experience | Click-through to websites | Direct AI generated answers |
| Optimization Methods | Keywords, backlinks, Technical SEO | Clear language, citations, structure |
| Ranking Factors | Authority, relevance, performance | Content clarity, trustworthiness |
The difference between GEO and SEO lies in their approach and purpose. SEO remains vital for organic traffic, but GEO is quickly gaining importance as AI-powered search changes how people find information online. For the best results, combining both strategies is essential.
Why GEO Matters Now — Trends & Data
The concept of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) has gained significance quickly with the increased use of AI-driven search technology. Conventional SEO is all about positioning pages in the search results, but with generative AI applications such as ChatGPT, the Search Generative Experience (SGE) in Google, and other large language models (LLMs), users are getting more and more direct and conversational responses rather than a list of URLs and jobs. This transition has resulted in a new phenomenon, so-called zero-click searches, meaning that users receive the answer without visiting any site. Recent research shows that zero-click searches have surpassed more than 50 percent of all Google queries in certain categories (Source: Search Engine Journal, 2025).
This shift compels creators of content to change their tactics. GEO makes sure your content is formatted and optimized in a way that it can be used in AI-generated answers, boosting your visibility, even when it did not gain the traditional click. With this fact being known by more companies and marketers, new tools and platforms that are specific to GEO are gaining momentum at high rates. As examples, the SEO.ai and Wix AI Visibility tools include functionality that is specifically aimed at guiding optimization to generative AI engines via AI citation tracking and answer surface measures.
Furthermore, generative AI is finding its way directly into the interfaces of major search engines, so knowing GEO becomes a major skill needed to keep up with the competition. SGE of Google is one example that combines the classical text search with the AI-generated attempts to summarize information for the user to provide a hybrid search experience that will require additional search engine optimization focal points.
In a nutshell, GEO is important today because AI is redefining the way people access information. Following this trend will enable companies and content providers to acquire AI traffic and remain well online in an AI-reading world.
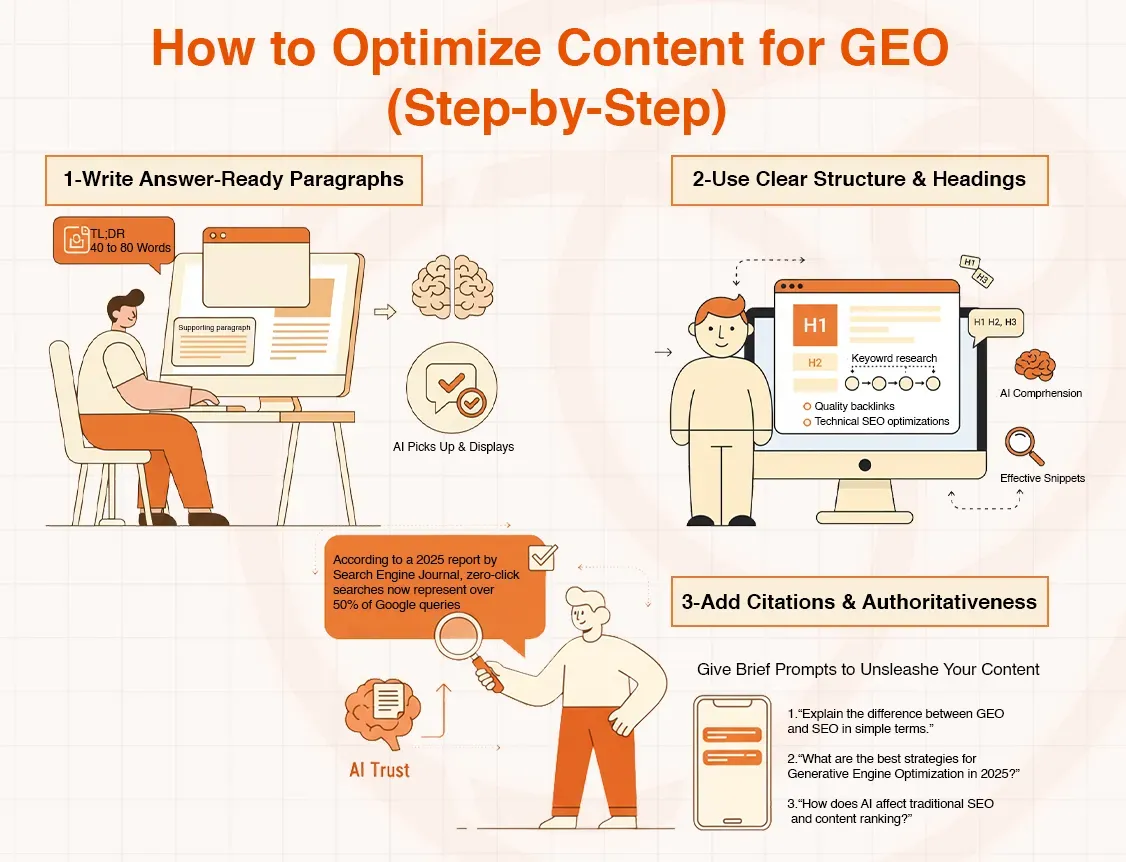
How to Optimize Content for GEO (Step-by-Step)
Let’s go with a practical step-by-step guide to optimize your content for GEO.
1-Write Answer-Ready Paragraphs
The AI models favour short, concise paragraphs that address the questions asked by the users directly. Your focus is on producing TL;DR (Too Long; Didn’t Read) summaries of 40 to 80 words, followed by one supporting paragraph to provide additional information.
For example: “SEO (Search Engine Optimization) the process of enhancing the visibility of your site on the search engines (the keywords, backlinks, and technical enhancement). It assists websites to rank better on Google and gain more organic traffic.”“SEO (Search Engine Optimization) the process of enhancing the visibility of your site on the search engines (the keywords, backlinks, and technical enhancement). It assists websites to rank better on Google and gain more organic traffic.”
Then add a second paragraph that describes the process in greater detail with examples and context. This format allows AI to pick up your content and display it as a straightforward response, especially when it comes to answering specific questions.
2-Use Clear Structure & Headings
Use mission statements, bullet points, or numbered lists and ensure you have clear headings (H1, H2, H3). This assists AI models in learning the rank and importance of your content. It facilitates the drawing of effective snippets. As an example, in the list of SEO techniques,s you must list:
- Keyword research
- Quality backlinks
- Technical SEO optimizations
This systematic process also makes you more user-friendly and gives you a better chance to be ranked both on Google and generic engines.
3-Add Citations & Authoritativeness
A good way to gain trust in AI is to add reliable quotations such as third-party websites, latest research, or the opinions of specialists. Links sources with dates- whenever possible enumerate the credentials of the author.
For example: “According to a 2025 report by Search Engine Journal, zero-click searches now represent over 50% of Google queries.”
- This indicates trust, enabling AI to rank your content higher when it comes to answering.
- Give Brief Prompts to Unleash Your Content
Enable users and AI systems to discover your content by giving them sample prompts they can enter in generative AI tools such as ChatGPT or Gemini.
Here are three examples:
- “Explain the difference between GEO and SEO in simple terms.”
- “What are the best strategies for Generative Engine Optimization in 2025?”
- “How does AI affect traditional SEO and content ranking?”
Including these prompts in your content encourages AI to recognize and surface your material in relevant queries.
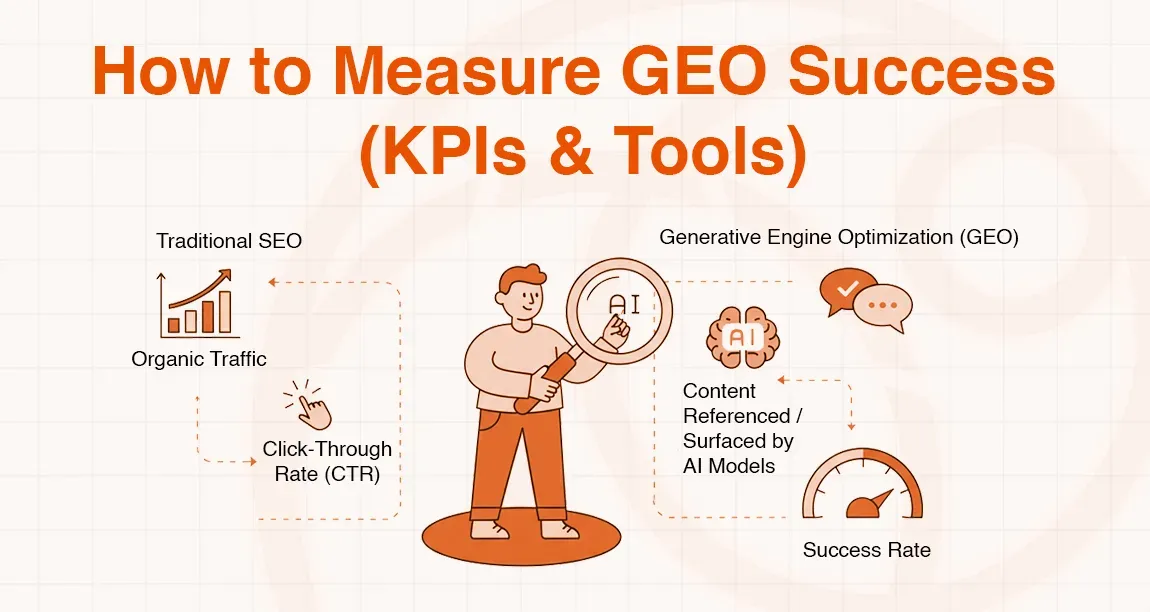
How to Measure GEO Success (KPIs & Tools)
To measure the success of the Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), it is necessary to monitor the following key performance indicators (KPIs), which show the success rate of your content in the AI-based search engine conditions. In contrast to traditional SEO, where organic traffic and click-through rate (CTR) are the main metrics, in GEO, you are concerned with how many times your content will be referenced or brought out to the surface by AI models.
Important GEO KPIs include:
- AI Citations: This measures how frequently generative AI tools reference or quote your content in their answers. A high number of AI citations indicates that your content is authoritative and trusted by AI engines.
- AI Impressions: Some emerging tools track how often your content appears in AI-generated results, even if users don’t click through. This reflects your brand’s visibility within AI search experiences.
- Brand-Mention Extraction: Tracking mentions of your brand or content in AI-generated text can help you understand your presence and reputation in AI-driven search.
These KPIs complement traditional SEO metrics such as organic traffic, bounce rate, and CTR, providing a fuller picture of your digital performance.
Tools to Track GEO Performance:
Various new resources have arisen to enable marketers to track GEO success. As an example, Wix AI Visibility will provide solutions to engagement patterns between AI platforms and your website. In the same way offers solutions that perform AI citation analysis and generate content that is optimized to pass through generative engines. SEO.ai Conventional SEO tools, such as SEMrush or Ahrefs, are also developing. There are now a few that provide minimal tracking of your large language model (LLM) citations or AI-led search statistics, with which you can estimate your GEO impact.
Conclusively, integrating these GEO-specific KPIs and tools with conventional SEO analysis will provide a complete strategy. This makes your content fit into the changing search environment to boost your presence across the artificial intelligence-generated responses and through normal searching.
Quick Case Example: How a Blog Snippet Was Transformed into an AI-Citable Answer
To understand the impact of GEO, let’s consider a simple case where a typical blog post snippet was optimized to become an AI-citable answer, increasing its chances of appearing in generative AI responses.
Before Optimization:
The original blog snippet was a long paragraph explaining SEO in general terms:
“Search Engine Optimization involves many techniques like keyword research, backlink building, and improving website speed to rank higher on search engines. It is important for businesses to increase their online visibility.”
While informative, this paragraph was too broad and lengthy for AI models to easily extract as a direct answer. It lacked a concise TL;DR style summary and structured formatting.
After Optimization:
The content was revised into a short, clear answer-ready paragraph followed by supporting details:
Optimized snippet:
“SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving a website’s visibility on search engines through keywords, backlinks, and technical improvements. It helps businesses rank higher on Google and attract more organic traffic.”
This was immediately followed by a brief explanation of core SEO tactics with bullet points. Additionally, an FAQ schema block was added to the page, signaling to AI engines that the content contains clear questions and answers.
Schema Added:
A JSON-LD FAQ schema was embedded, marking up common SEO questions and their concise answers. This structured data helped generative AI tools easily identify and cite the content when users asked related queries.
Result:
Within weeks, the optimized snippet started appearing as a featured answer in AI-powered tools like ChatGPT and Google’s Search Generative Experience, driving more visibility and indirect traffic even if users did not click the link directly.
GEO & SEO Checklist
To effectively optimize your content for both Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO), follow this comprehensive checklist:
- Write concise, answer-ready paragraphs (40–80 words)
- Use clear and logical headings (H1, H2, H3)
- Incorporate keywords naturally throughout the content
- Add authoritative citations with source links and dates
- Implement FAQ schema using JSON-LD
- Structure content with bullet points and numbered lists
- Provide AI prompt templates to help surface your content
- Optimize metadata (titles, descriptions) with target keywords
- Build internal links between related pages
- Acquire high-quality backlinks from reputable sites
- Monitor AI citations and impressions with GEO tools
- Use hybrid SEO tactics to complement GEO strategies
This checklist is designed to guide beginners in adapting their content for the evolving search landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I would state that GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) and traditional SEO are crucial pillars in the digital marketing world of the present day. Whereas SEO assists you in achieving a better position on traditional search engines, GEO is aimed at optimizing your content to appear on AI-based search services such as ChatGPT and the Search Generative Experience that Google offers.
To the beginners, it is important to learn how to apply both strategies. Use of SEO or GEO alone is not sufficient, but using the two together leads to a hybrid in which your content is given greater reach and visibility.
The most essential thing is to create short and proper content that can be used by the AI engines as well as humans. Also, it is crucial to track any applicable KPIs and employ the latest tools, which will help you keep up in this changing environment. Considering both GEO and SEO would allow improving the online presence and ranking at the top of AI-driven and classic search systems