A Definitive Guide to AI Marketing: From Foundations to Future-Proofing
TLDR: AI marketing is transforming traditional strategies, using machine learning and generative AI for hyper-personalization, automation, and predictive insights. It greatly increases ROI, enables marketers to be strategic, and requires ethical governance to be successful and trusted in the long-term.
A Definitive Guide to AI Marketing: From Foundations to Future-Proofing
There is a radical and paradigmatic change in the marketing sector where the traditional mass-based strategies are being overturned by a new paradigm of data-driven precision of artificial intelligence (AI). Historically, traditional marketing strategies were founded on mass-media like TV, radio, billboards, and newspapers to deliver the same message to large numbers of people, hoping that a small percentage of the mass audience would consider that message interesting enough to act on. This approach was push-based, and decisions were made on the basis of general demographic information and individual judgment on what such a broad-based consumer would find interesting enough to act on.
AI marketing is an absolute contrast to this model. Its intelligence source is the primary point of divergence: reasoning and advice generation is realized with the help of sophisticated computer algorithms as opposed to human intuition, which the traditional methodology cannot possibly offer. Rather than a broad-narrow approach, AI can be used to establish a more direct and personal connection, anticipating needs and contextualizing messages even before the customer has articulated intent, and it is a game-changer enabling AI to be more precise and effective than ever before. This shift does not make traditional marketing irrelevant--it is still relevant and commanded a significant portion of ad spend back in 2021--but AI is a game-changer that is more precise and effective than ever before.
What Is AI Marketing? A Comprehensive Definition
AI marketing can be described as a type of marketing in which marketing teams employ artificial intelligence concepts and models, such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision, to deliver on strategic marketing objectives. In its broadest sense, AI marketing involves the systematic implementation of the capabilities of AI, including data collection and data-driven analysis, to elicit applicable insights into customers and automate key marketing decisions.
Contemporary AI solutions have allowed a broad range of usages, including automating repetitive work-flows and creating content, as well as doing audience segmentation and consumer data analysis to make the efforts involved in content marketing more effective and customer-facing communications more autonomous. Businesses are using AI to optimize social media posts, improve email marketing, and perform better scanning of consumer data to gain deeper insights.
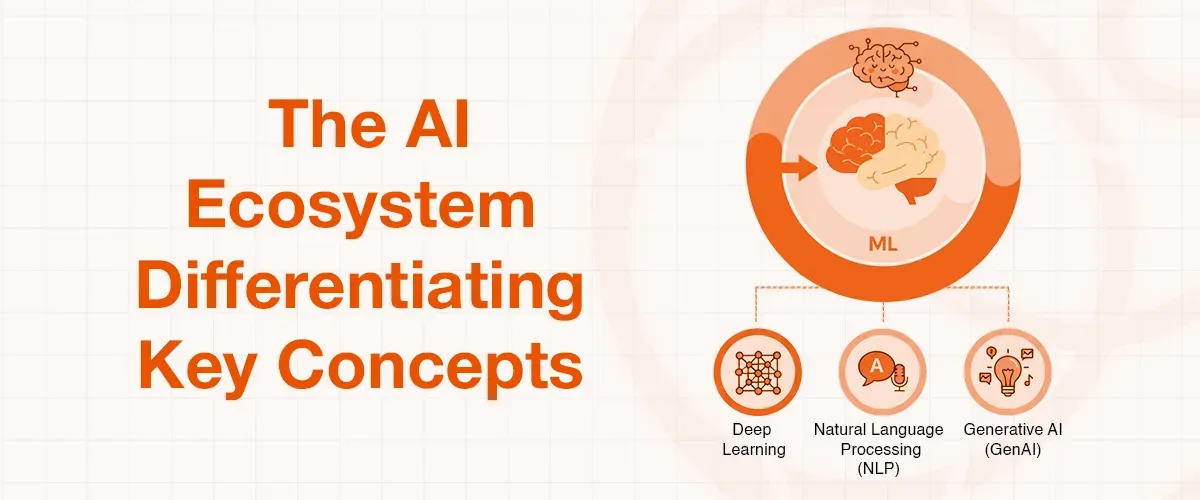
The AI Ecosystem: Differentiating Key Concepts
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are used interchangeably, although they represent different elements of the same technology ecosystem. AI is an umbrella term indicating that computer software can mimic the mental capabilities of humans, such as analyzing, reasoning and learning to take on complex tasks, machine learning, in turn, is a subset of AI, which implies that an algorithm trained on data can create a model to execute such tasks.
This difference expresses a more insightful intelligence of marketing that is changing. AI concerns the situation when complex tasks are regarded as reasoning and mimicking human thought, whereas the goal of ML is to process large amounts of data and then find patterns with a specific probability of being correct. This implies that marketing intelligence is no longer just about human creativity or intuition but a combination of human strategic foresight and the ability of the machine to process, predict and customize on a scale that has never been imagined before.
Other important sub-fields to consider are the AI marketing ecosystem:
- Deep Learning: A more sophisticated form of ML which applies artificial neural networks, inspired by the human brain, to carry out complex reasoning problems without human assistance.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is a field of study that aims to make software interpret, understand,tand and generate human communication that is important in a chatbot or sentiment analysis.
- Generative AI (GenAI): This form of AI operates on the principles of large language models (LLMs), and is applied to generate new content text, images, and other media in a dynamic response to user prompts.
When these technologies are together they form an impressive array of tools that automate, predict, and personalize marketing ventures with more accuracy than ever before.
Table 1: AI vs. Traditional Marketing Comparison
| Metric | Traditional Marketing | AI Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Mass-based campaigns | Hyper-personalized campaigns |
| Targeting | Broad demographics, mass audience | Micro-segmentation, individual behavior |
| Data Utilization | Limited data (surveys, focus groups) | Real-time Big Data, consumer insights |
| Decision-Making | Human intuition and creativity | Algorithmic insights, predictive analytics |
| Efficiency | Slower campaign management | Automated, real-time optimization |
| Cost | High upfront costs | Cost-effective over time |
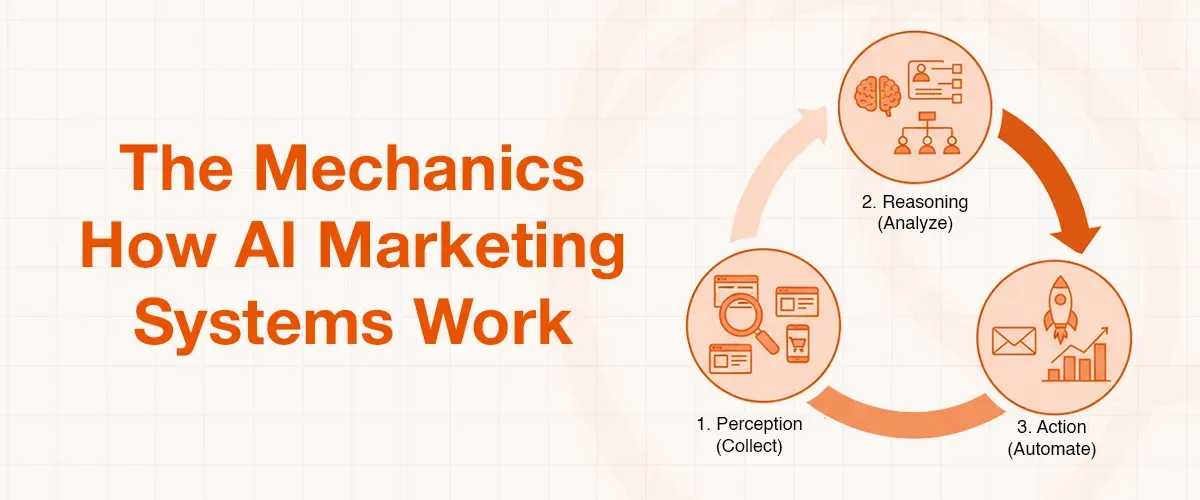
The Mechanics: How AI Marketing Systems Work
The Algorithmic Engine: The "Collect, Reason, Act" Cycle
The AI marketing systems operate on the concept of the perception-reasoning-action cycle of cognitive science. This is a three-step process that is the basic model of how AI converts raw data into strategic marketing results.
- Perception (Collect): The first step in the cycle is the ongoing gathering of huge volumes of information through the many sources at our disposal. This information may consist of the browsing history, the buying habits, the place, the social media activity, and other Internet interactions of a customer. This baseline step gives the AI the raw material on which it can analyze and learn.
- Reasoning (Analyze): AI processes the data, which is collected with the help of sophisticated machine learning algorithms. Here the essence of "intelligence" is put into play. The AI condenses information in the huge datasets, finding the patterns and trends in users. As an example, user data can be processed using a personalization engine to recognize segments of users that may have common behaviors or interests, which are then split up to target content.
- Action (Automate): The last stage is to make the AI act on the conclusions it has made. This may be in the form of automating a decision like a personalized email or as a recommendation to a human marketer, such as in real-time adjusting an ad bid. This automated implementation is the end game because with this, marketers will be able to work with a speed and precision that cannot be achieved with manual procedures identified as the sole ones.
Data as the Catalyst: From Silos to Strategic Insight
The quality and quantity of data that an AI system is working with determines its efficacy directly. One of the main problems of the modern marketer is how to use the sheer volume of data at his or her disposal when planning campaigns, which tends to be disjointed and held in detached silos. AI provides a solution by automatically collecting, aggregating, and centrally storing valuable marketing data across all platforms and systems, including CRM software, site analytics, and sales platforms. This can be used to feed AI with reliable data in real-time, providing AI with the ability to deliver meaningful insights and personalized customer experiences on demand.
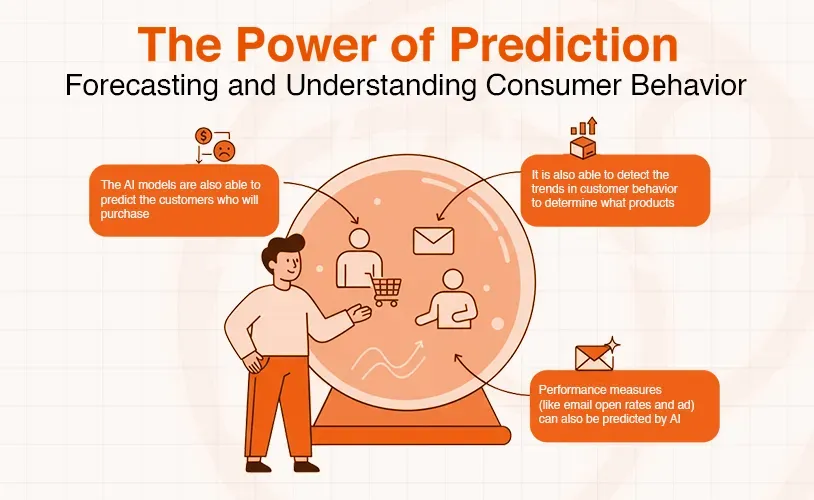
The Power of Prediction: Forecasting and Understanding Consumer Behavior
Predictive analytics is a major element of the reasoning stage. This is a type of analytics that is based on historical data and algorithms of AI to predict the future trends and results. As the AI can analyze large volumes of customer data in a few seconds and produce insights on the future consumer behavior, marketers can make data-driven and proactive decisions and streamline their processes.
Predictive analytics capabilities are broad:
- The AI models are also able to predict the customers who will purchase or those who are prone to churning so that a business can implement specific campaigns to retain them.
- It is also able to detect the trends in customer behavior to determine what products could do well and maximize pricing options in real time.
- Performance measures (like email open rates and ad interactions) can also be predicted by AI in digital campaigns, enabling better lead scoring and general strategy.
This vision is a business revolution as companies are able to foresee customer needs, risk reduction and avoid being caught off-guard due to market changes. Predictive analytics is not only about looking into the future, but it allows drawing a direct cause-and-effect relationship between foresight and strategic agility. With awareness of the most likely leads to convert, a sales team can focus its effort and become more efficient. This shows that AI is turning marketing into a more proactive discipline, rather than a reactive one, that is, campaigns are initiated and optimized, based on an intelligent prediction of what the market needs.
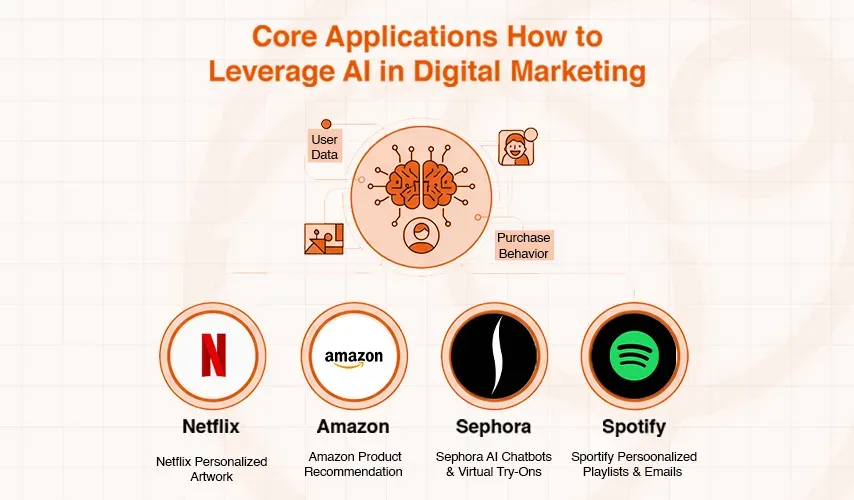
Core Applications: How to Leverage AI in Digital Marketing
Hyper-Personalization: Crafting the One-to-One Customer Journey at Scale
Hyper-personalization is one of the most impactful ways to use AI in marketing to offer an individualized experience to each individual consumer to the extent that the company has never engaged in such behavior before, analyzing the user data, browsing history, purchase behavior and demographic data and creating a personalized content that appeals to the interests of a specific consumer which leads to better customer satisfaction and increased brand loyalty and higher conversion rates.This strategy succeeded spectacularly with leading companies:
- Netflix applies AI to the content that it personalizes when it comes to artwork in movies and shows. To a viewer who frequently watches action movies, the same film can be promoted with an image that features an action-heavy moment, but a different viewer who watches more comedies would see an image depicting a funny moment. The company aims to enhance the rate of conversion and enrich the viewing experience of the visitors to its service.
- In 2003, Amazon became one of the first companies to use item-to-item collaborative filtering, and today, its recommendation system is credited with an estimated 35 percent of its sales.The AI identifies products on a customer's screen that the person is most likely to turn them into a fan instead of a casual browser.
- Sephora used AI chatbots and a Virtual Artist App in promoting its large product line-up. The app offers personalized tips and product recommendations in response to the user input which led to a sharp rise in the e-commerce sales and a 11-percentage point better conversion rate on booking in-store makeovers.
- Spotify follows the same strategy as Netflix, when it analyses user data to create personalized playlists and send automated and personalized messages in email marketing.
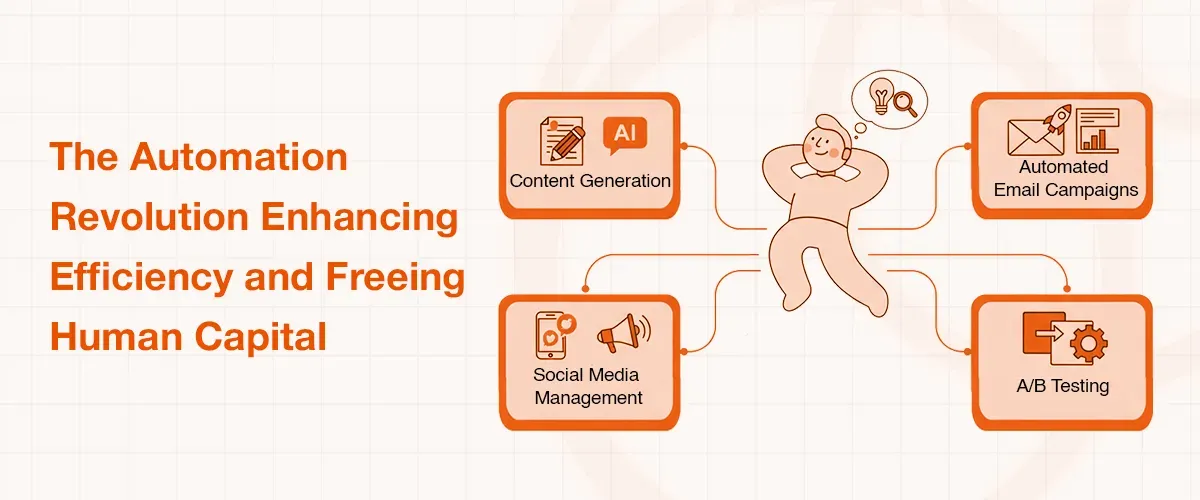
The Automation Revolution: Enhancing Efficiency and Freeing Human Capital
One of the fundamental advantages of AI is that it can help automate tedious and time-consuming processes, which does not only enhance efficiency, but also enables marketers to shift their time and effort toward more high-value and strategic processes.
Important spheres of automation are:
- Content Generation: Generative AI systems such as ChatGPT or Claude can generate marketing content of all types: blogs, website copy, emails, and advertising copy, saving marketing teams money and time. The technology can also translate content into other languages or generate consistent variations of a campaign across platforms.
- Automated Email Campaigns: AI-driven marketing automation is able to assess customer behavior, tastes and demographics to target them with personalized messages and tailor subject lines to more open and click-throughs.
- Social Media Management: Social media listening is automated and content scheduling is automated. They track brand mentions and customer sentiment in real time with the help of NLP and sentiment analysis to aid with reputation management and competitive intelligence.
- A/B Testing: AI can perform quicker and more extensive A/B testing than humans, executing campaigns using algorithms to optimize all aspects of web copy and design, in addition to calls-to-action, as AI learns, the process becomes more instinctual and the results more informative.
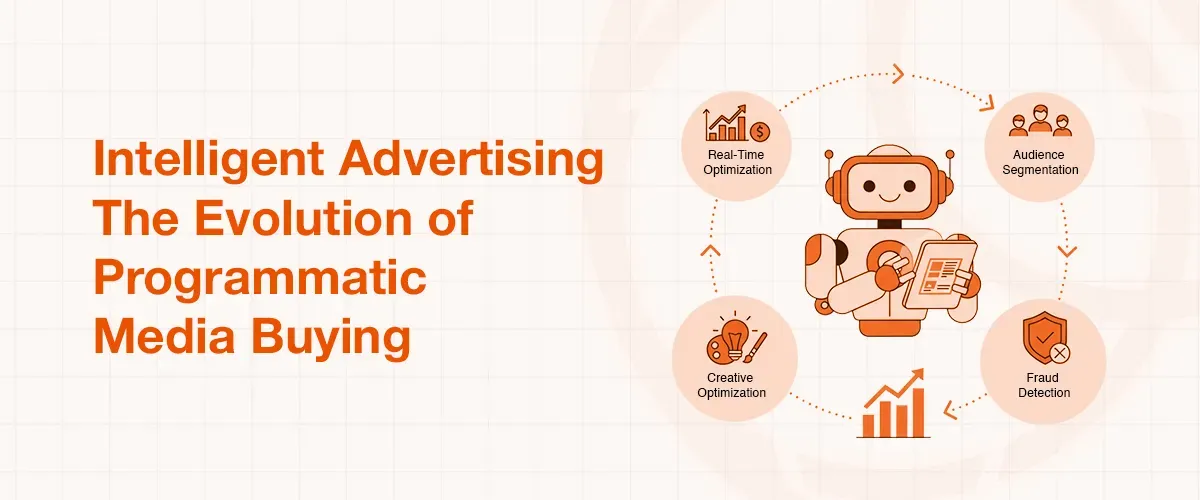
Intelligent Advertising: The Evolution of Programmatic Media Buying
AI and machine learning have fundamentally improved programmatic advertising, the automation of the process of buying and selling digital ad space. AI algorithms work behind the scenes to optimize data across many dimensions, including ad format, device type, and geography. It has the result of improving the mapping of ad inventory to the appropriate targeted audience at the appropriate time.
The application of AI in programmatic advertising can involve:
- Real-Time Optimization: AI supports real-time ad campaign optimization and bidding strategies, which helps advertisers in optimizing their return on ad spend (ROAS).
- Audience Segmentation: AI delivers highly performing audience segments that have never existed before with a high degree of accuracy and precision of delivering ads to those customers who are most likely to convert. It is also able to segment customers using complex behavioral data that is even greater than simple demographics.
- Creative Optimization: Being a high-performance assistant, AI is able to interpret trending themes in the market and the audience preferences to improve ad creatives content and relevance.
- Fraud Detection: AI can be used to identify and stop fraud, e.g., when a single IP address suddenly generates a large number of clicks. Artificial intelligence (AI) has been trained to identify and stop fraud using machine learning algorithms when trained on historical data. This helps to make sure that the campaign data in question is founded on the actual engagement and retains a positive status with ad networks.
Optimizing the Customer Experience: AI in Service and Support
The impact of AI can be directly transferred to the customer experience whereby all customer touchpoints are improved in terms of the first point of contact and after-sale services. AI and chatbots give 24/7 customer service, answering common questions and directing consumers to the data they seek. This relieves human customer service staff of less complex problems.
In addition, AI-based sentiment analysis can filter through large volumes of text-based social media, online reviews, and customer responses to isolate underlying attitudes and emotions to enable companies such as Starbucks to detect customer sentiment in the moment, trending topics, and act on feedback, which is vital to reputation management.
Table 2: Key AI Marketing Applications & Benefits
| Application | Example/Company | Core Benefits/Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Personalization | Netflix, Spotify, Amazon | Increased conversion rates, enhanced customer satisfaction, 35% of Amazon sales from recommendations |
| Programmatic Advertising | Audi, Coca-Cola | Higher ROAS, cost-effective media buying, fraud detection |
| Content Generation | The Washington Post, Oxa | Time and cost savings, consistent brand voice, multilingual content creation |
| Customer Service | Sephora, Starbucks | Enhanced customer experience, 24/7 support, 11% higher conversion for Sephora makeovers |
| Predictive Analytics | Target, Optimove | Proactive strategy, improved lead scoring, reduced customer churn |
The Profound Impact: Benefits and Transformation
Tangible Gains: Measuring the ROI of AI Marketing
The effect of the AI in marketing is not just theoretical, but it is measurable and leads to the provision of substantial practical advantages. The AI in marketing market is growing at a rapid rate, with a projected value of over $217 billion by 2034, and evidence shows that organizations using AI as the basis of marketing campaigns experience a 20-30% increase in ROI as compared to those that use traditional marketing tools. 81% of marketers who have adopted AI note that this is an essential tool for driving brand exposure and direct sales.
But to determine this value accurately , one needs a more complex methodology that goes beyond the measures of simple vanity such as click-through rates. The value of AI may compound over time, and its impact may be felt throughout the customer lifecycle. To get an accurate determination of this value, a holistic approach becomes essential that goes beyond the measure of simple vanity metrics such as click-through rates.
Total AI ROI= (Revenue gains + Cost savings + Retention benefits + Operational efficiencies)[?]0=Total AI costs
This equation has a revealing critical point: The entire value of AI is not in one specific use, but in its systemic application throughout the marketing role. The advantage is that it has a compounding effect that boosts revenue, retention and operational efficiency and thus its actual payback is a reflection of its ultimate role, not of a single campaign parameter.
The Changing Role of the Marketer: From Task-Doer to Strategist
The fast pace of AI implementation has inevitably brought up questions about its effects on the job roles in marketing. The evidence indicates the presence of a unified opinion: AI will not replace marketers, but transform their professional activities fundamentally, as it will do away with routine work and allow professionals to concentrate on the strategy, how to be creative and risky. According to a survey conducted by The Conference Board, 75% of businesses think AI will change their marketing roles but not eliminate them since it will remove repetitive tasks and enable the professional to focus on the strategy, how to be creative and risky.
AI is best in data-based, repetitive activities, including data acquisition, content generation, and more basic reporting. By automating their low-impact activities, AI allows marketers to focus their efforts on strategic work and creative activities. The ability to connect emotionally, empathize and come up with creative geniuses that are uniquely human, becomes the most valuable currency in this new world, and that AI cannot reproduce; it must be adopted as a collaborator and not a competitor by marketers.
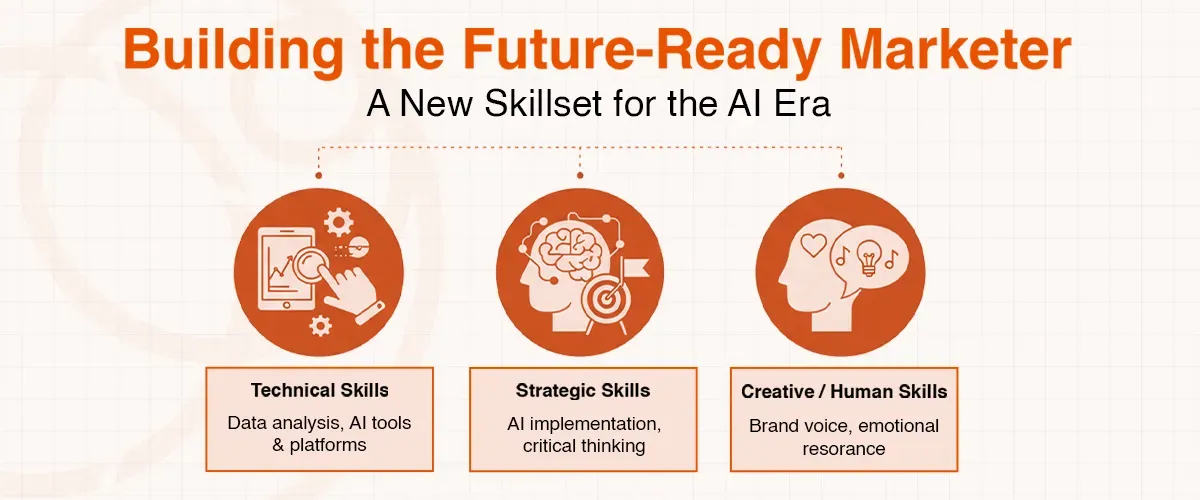
Building the Future-Ready Marketer: A New Skillset for the AI Era
In order to succeed in the marketing environment developed on the basis of AI, an individual will have to develop a new range of skills that will either complement or enable the use of AI. These abilities are a combination of technical expertise, thinking strategically and the creative ability of a human being.
- Technical Skills: Marketers need to become skilled in data analysis and visualization, and can make data-based decisions or interpret AI-generated insights based on a basic understanding of the principles of machine learning and the capabilities of AI tools. They also need to be skilled at using AI-driven tools to create content, manage social media, and automate marketing.
- Strategic Skills: The key one is the development of strategies of AI implementation, which should be based on the overall business goals and objectives, and this requires that the marketers are adept in strategic planning and critical thinking to establish the vision and objectives that AI systems will achieve. The capability of planning and critical thinking has now become essential, as compared to intuition-based assumptions.
- Creative / Human Skills: Although AI can write content, it cannot develop brand voice, make the content engaging, or create emotional resonance; these are the uniquely human skills that will distinguish the most successful marketers of the AI era.
Table 3: The Evolving Marketing Skillset
| Skill Area | Automated/Enhanced by AI | Critical Human Skill |
|---|---|---|
| Data Analysis | Data collection, basic reporting | Data interpretation, ethical oversight, contextual understanding |
| Content Creation | First drafts, content optimization, translation | Brand voice, creative direction, strategic storytelling |
| Campaign Management | A/B testing, ad scheduling, lead nurturing | Strategic planning, campaign ideation, defining objectives |
| Strategy | Audience segmentation, predictive modeling | Intuition, problem-solving, market trend analysis |
| Customer Interaction | Routine inquiries, FAQ answers | Empathy, relationship building, handling complex issues |
The Imperative of Responsibility: Navigating Ethical Challenges
The massive potential of AI in marketing is also coupled with serious ethical obligations that should be taken care of. Lack of taking such issues into consideration may result in consumer backlash, legal consequences and brand damage.
Privacy and Consent: The Data Dilemma
The paradox of AI marketing systems is that, on the one hand, huge volumes of data can make AI systems more accurate; on the other hand, on the one hand, it has created an additional possibility to violate privacy rights because AI does not need a person, just a large amount of data, to work with information.
Legal regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) provide people with rights to their own personal data including the so-called right to erasure, but this brings a special challenge to AI systems, especially large language models, which introduce personal data deep within the system and makes it almost impossible to erase. One such area of concern is the so-called repurposing of personal data - taking data that has been gathered with one intent, and using it in an entirely different, and often unknown, way without any prior authorization. This event underscored the importance of improved data security, disclosure and data control by users in AI-based platforms.
Algorithmic Bias: The Unseen Pitfall
Systematic and repeatable AI errors that produce unfair results, typically based on biased or unrepresentative training data, are referred to as algorithmic bias since AI systems can only be as good as the data they are trained on, skewed data will tend to unfairly favor some demographics and leave out or misrepresent others.
Live-life cases of this are many and alarming:
- Recruiting Instruments: The AI recruiting tool created by Amazon was discovered to be discriminative against women, scoring resumes including words such as women's low since the historical information it was trained on represented male applicants.
- Ad Targeting: A research done on the online advertising system by Google revealed that high paying jobs were targeted more often to men by almost six times that of women. Female profiles were instead advised to work in generic, low paying jobs.
- Recommendation Engines: Have the ability to promote a general social stereotype, whether it be related to race, gender, or socio-economic status. Such as the e-commerce recommendation engines suggested by AI might not show luxury products to users in higher-income regions or not show luxury products to a certain group of users.
The effects of such prejudices cannot be underestimated and continue to perpetuate prejudice in society, generate discriminatory effects, and lead to irreparable damage to a brand image.
Transparency and Trust: The Path to Ethical AI
Other important ethical factors include transparency, other than privacy and bias. Consumers must know when they are dealing with an AI system and when they have been presented with AI-generated information or content or influenced by an AI to make a choice. One of the most striking cases was the controversy of Gobelins Paris, a French art school, that employed AI-generated images in its marketing but did not mention them. This absence of transparency was considered to be a breach of trust on a body focused on human creativity, which emphasizes the need to disclose the information so as not to be criticized by people.
Similarly, and just as qualitatively considered, in the case of the IBM Watson controversy where AI generated dangerous cancer treatment prescriptions without sufficient human interventions, fairness, and a strong data protection policy should be viewed as a prerequisite to brand building and sustainable long-term development.
Table 4: Ethical Concerns and Real-World Examples
| Concern | Description | Example Case Study | Broader Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Privacy & Consent | Misuse of data collected without consent | Facebook-Cambridge Analytica | Legal scrutiny, loss of consumer trust, regulatory fines |
| Algorithmic Bias | Discriminatory outcomes from biased training data | Amazon's recruiting tool | Perpetuating societal prejudices, brand reputation damage |
| Lack of Transparency | Failure to disclose AI use in content or processes | Gobelins Paris | Public backlash, eroding authenticity and brand trust |
Conclusion
Not a trend, AI is the foundation of the next generation of marketing. The paradigm shift that is taking place within the industry is a result of AI where the massive campaigns are being substituted with hyper-personalized and data-driven customer experiences on a scale that was once unimaginable. The statistics validate this truth: AI is resulting in high ROI, efficiency, and customer engagement. It possesses the ironic purpose of humanizing and personalizing marketing by the use of one-to-one communication and accuracy never previously experienced.
The marketing organization of the future ought to know that this revolution does not mean that they are replacing human marketers but empowering them. The most valuable marketers will be a new set of rules (a new playbook) to combine smart technology and the power of human ingenuity. Who can lead the AI systems to a strategic vision to endow their output with emotional attractiveness and creative genius that can be provided only by a human being.
The way forward to be successful in this new terrain is a commitment to three areas:
- Strategic Investment: AI tools with hyper-personalization and real-time insights have to be invested in by organizations. This new model has to be supported by their technology infrastructure.
- Talent Development: It is essential to enhance the talents of the marketing teams. They are required to acquire technical and strategic expertise in order to collaborate with AI efficiently and handle the tasks that it enables of higher value.
- Ethical Governance: It is necessary to establish a powerful ethical code that meets the requirements of data privacy, algorithmic bias, and transparency. This is not a compliance check list. It is required in order to build consumer confidence and long-term growth.
It is projected that by 2030 the global market of generative AI will be more than $356 billion. This demonstrates that there is no choice but the need to embrace AI. The future is in the hands of those who consider AI not as a menace but as an instrument of a more efficient, effective and human-oriented marketing practice.