Beginner's Guide to Machine Learning in Marketing
TLDR
Machine learning is a business necessity that is changing marketing into an action discipline that is more predictive than reactive. It uses algorithms to process large amounts of data, making it hyper-personalised, predicting leads, and churn forecasting proposals and programmatic optimization of advertising. The adoption of ML models has ceased to be an option; it is its essential ingredient for high ROI and sustainable competitive advantage
Have you ever wondered how Netflix knows exactly what show you’ll be interested in binge-watching next? Or how Amazon offers you a list of the products that you might like that seems to have been read out of your mind? The real magic behind this is not psychic, but machine learning in marketing.
To most people, machine learning evokes the idea of sophisticated code and robotic science fiction. However, in an actual sense, it is a strong and available tool that is transforming the marketing arena. This guide will break down machine learning to you, and define what it is, why it is important, and the ways it is already being used to make marketing smarter and more effective in both large and small businesses.
What is Machine Learning?
Basically, machine learning (ML) is a subdivision of artificial intelligence in which computers are taught to recognize trends and make individual decisions through data, without being explicitly trained to perform each task separately.
Consider it as training a child to recognize a dog. It is not a long list of rules you write like: there are four legs, a tail, and fur on it, it is a dog (a cat can fit that description as well). Rather, you present to the child hundreds of pictures of various dogs, big ones, small ones, fluffy ones, short-haired ones. With time, the child's brain gets to learn the underlying patterns and can correctly recognize a dog it has never seen.
The same happens with machine learning. We are giving a computer algorithm enormous loads of data in the marketing field, this data might be previous customers' buying history, website clicks, email opens, and social media interaction.
This historical data is used to create predictions by the algorithm, which learns from this information. The idea is not to go by a programmed set of rules but to understand complex patterns, which a human would not see.
Why Machine Learning is a Game-Changer for Marketing Analytics
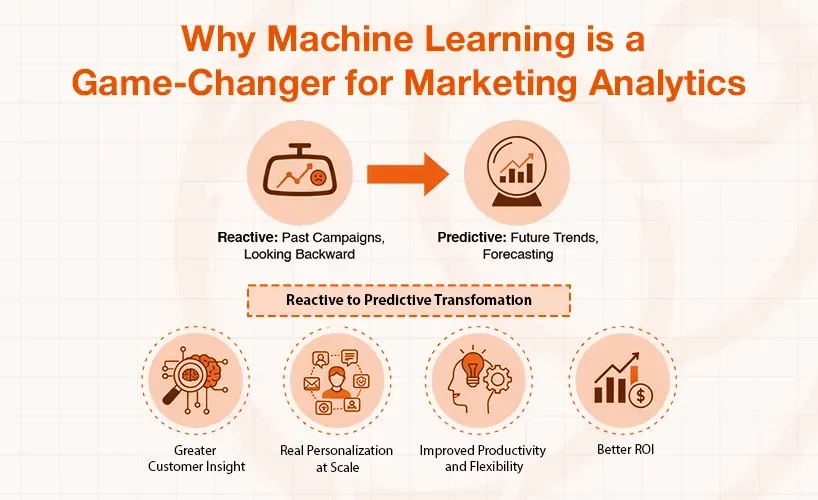
For decades, marketing analytics has been mainly like looking in the rearview mirror. The marketers would review the performance of the past campaigns and identify what worked and what failed. This has been useful, but it is also reactive. Machine Learning in marketing analytics reverses the script and enables the marketer to move into the future and forecast on what will occur.
Such a reactive-to-predictive analytics transformation comes with many massive benefits:
- Greater Customer Insight: Humans can identify trends on a spreadsheet, but ML algorithms can analyze millions of data points at the same time to identify more subtle and hidden trends in customer behaviour. This results in far better insight into your customer and their desires.
- Real Personalization at Scale: Old-fashioned personalization may imply the use of a client's first name of a client in an email. The personalization through ML may be applied to the whole customer experience, i.e., the types of ads a certain user is shown, the recommendations a user is offered on a website, the services the user is offered in a mail, etc., all of the product suggestions, depending on the behavior of the user.
- Improved Productivity and Flexibility: ML can automate complicated and data-heavy procedures that would require a human team to spend countless hours. This makes marketers organize and be creative rather than lose their heads in manual data analysis.
- Better ROI: Machine learning will assist you in using your marketing budget in a better and more reasonable manner because it will identify the leads that are likely to convert, customers who are likely to churn, and the ad channels that will provide the best ROI.
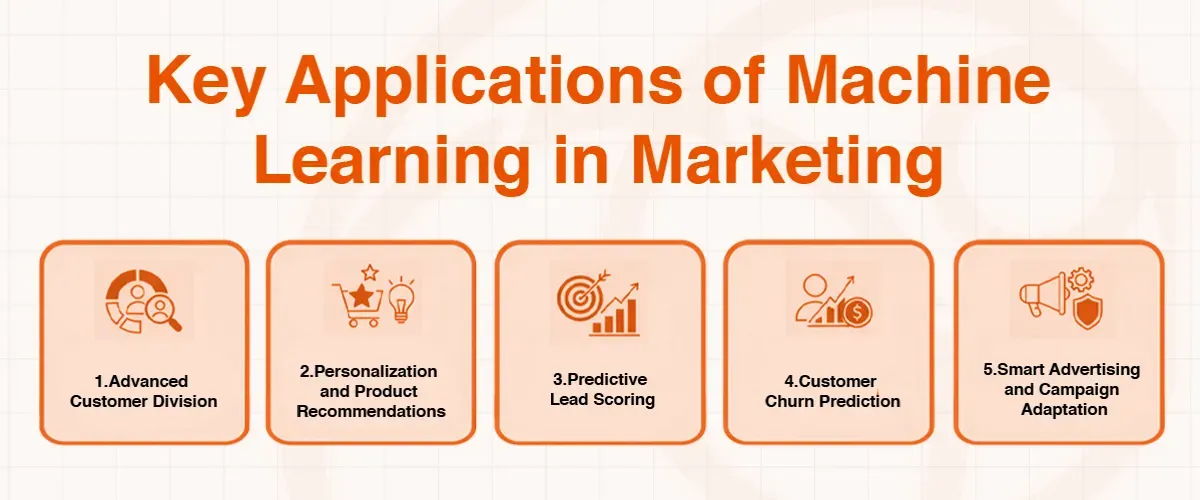
Key Applications of Machine Learning in Marketing
Then how does all this work in the real world? The application of machine learning in marketing is immense and expanding. These are some of the most effective ways it is currently being applied.
- Advanced Customer Division: Marketers have always divided their target markets according to their demographics, such as age, gender, and place. Machine learning takes this to the next level. ML models can categorize customers using algorithms such as clustering, which incorporate the real behavioral tendencies of the customers, including their browsing tendencies, the frequency of purchases, and their interaction with brands. This produces dynamic, nuanced groups such as high spending loyalists, at-risk bargain hunters, or newly-engaged browsers, and much more specific and relevant messaging can be created.
- Hyper-Personalization and Product Recommendations: It is among the most apparent applications of machine learning in AI-powered digital marketing. The ability to recommend relevant products, articles, and videos with such precision is due to the use of recommendation engines that are driven by methods, such as collaborative and content-based filtering (suggesting products/articles/videos similar to those a user liked in the past). This not only enhances a better customer experience, but also enhances the cross-selling and up-selling opportunities significantly.
- Predictive Lead Scoring: ML models can use the features of your previous successful customers and score a new lead on whether they will convert or not. These AI agents may get to know that during the downloading of a particular whitepaper and visiting the pricing page thrice, the leads are 90 percent more likely to purchase. This enables the sales teams to focus on the hottest prospects.
- Customer Churn Prediction: It is a lot more costly to acquire a new customer than to retain one. Customer behavior can be analyzed using machine learning models to detect customer signals that they are a potential churner (e.g., reduced activity, fewer purchases, visits to the cancellation page). The marketers are then in a position to intervene proactively with specific retention offers or support to retain that customer.
- Smart Advertising and Campaign Adaptation: AI has transformed the way brands reach customers online through effective advertising campaigns, such as:
- Programmatic Advertising: The majority of ads you see on the internet are bought through programmatic bidding. During the milliseconds it takes a webpage to load, the ML algorithms look at the information of the user, the worth of showing them an advertisement, and make an actual-time bid with the other advertisers in that spot.
- Ad copy and creative optimization: ML can test thousands of potential combinations of headlines, images, and call-to-action buttons at once to figure out what version will perform best on various segments of the audience. This is much deeper than the customary A/B testing, and the effect of continuous and automatic improvement of a campaign is achieved.
- Dynamic Pricing: E-commerce and travel websites implement machine learning to dynamically set prices depending on their aspects such as demand, pricing by competitors, time of the day, and even the browsing history of a user.
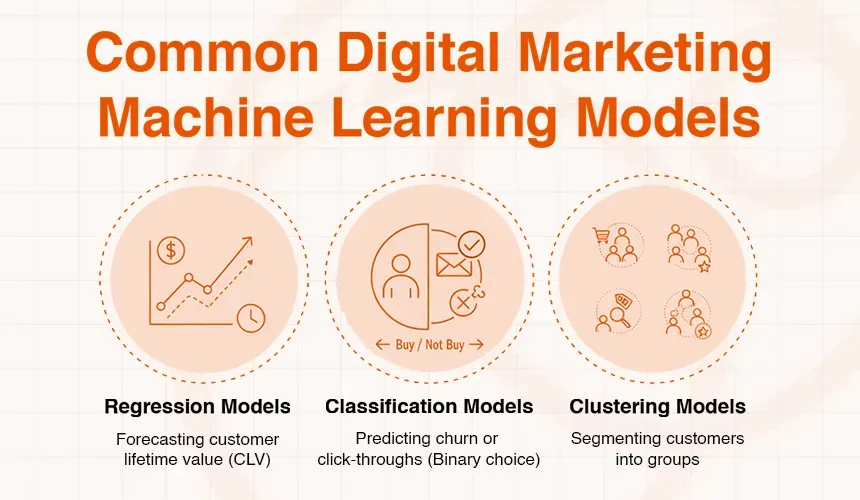
Common Digital Marketing Machine Learning Models
There is no need to be a data scientist in order to be a marketer, although it helps to be familiar with the terminology. The following are some of the typical digital marketing machine learning models:
- Regression Models: They are employed to forecast a continuous numerical estimate. As an illustration, forecasting the lifetime value of the customer (CLV) or the amount they would spend during their next purchase.
- Classification Models: This is applied when a category is to be predicted. Binary classification (two choices) is the most frequently used, e.g., whether a customer will churn or not churn, or whether an email receiver will click or not click.
- Clustering Models: Clustering models are applied in unsupervised learning, where similar data points are clustered. It is the algorithm that is powering the highly customer-segmented discussion above, where the algorithm identifies the natural clusters within your customer base without any guidance on what to find.

Conclusion
Machine learning in marketing is not a buzzword anymore, but a part and parcel of an effective and efficient marketing strategy today. The use of data to predict customer behavior, automate decisions, and provide genuinely personalized experiences can help businesses establish a stronger relationship with the customer and gain a great competitive edge. A marketer does not need to be a programmer to learn how to create the algorithms, but to understand their abilities is the first step to the superhuman powers they hold.